Direct-to-Dish 2026: Next-Gen Viewer Access

Direct-to-Dish 2026: Next-Gen Viewer Access
Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
In 2026, the broadcasting world is witnessing a dramatic comeback of the satellite dish — but smarter, faster, and more connected than ever. The new Direct-to-Dish (D2D) technology delivers content straight from orbit to viewers without the need for cables, broadband, or local internet dependency.
By integrating AI-driven signal routing and adaptive compression, Direct-to-Dish streaming brings IPTV-level interactivity and quality directly to households worldwide — redefining accessibility and performance in modern broadcasting.
📡 What Is Direct-to-Dish 2026?
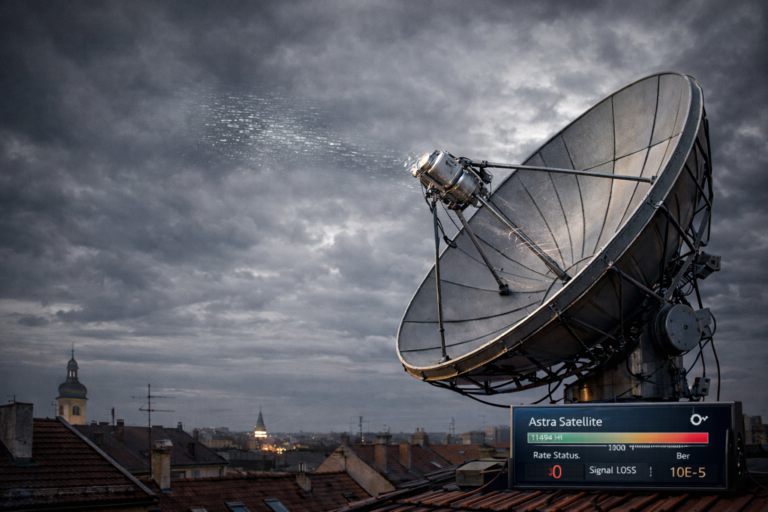
Unlike traditional satellite TV, where signals pass through multiple relays before reaching your home, the new D2D architecture connects viewers directly to low-orbit satellites. These satellites deliver encrypted data streams that can be decoded by smart receivers or AI-enabled dishes with built-in processing chips.
This allows real-time transmission of HD, 4K, and even 8K channels — bypassing terrestrial bottlenecks entirely. The result is instant access, minimal delay, and maximum reliability, regardless of geography.
⚙️ How Direct-to-Dish Works
Each satellite continuously transmits content across adaptive frequency bands optimized by artificial intelligence. The dish at home automatically locks onto the strongest beam, using machine learning to adjust positioning and reduce interference from weather or obstacles.
Data is processed locally, meaning users experience IPTV-grade responsiveness without needing high-speed fiber or 5G. This is particularly transformative for rural or remote regions still lacking robust infrastructure.
💡 Key Advantages of D2D Technology
- Instant Access: Connects directly to orbit without third-party networks.
- Low Latency: Real-time switching enables seamless live events.
- AI Optimization: Intelligent routing enhances quality and stability.
- Universal Coverage: Works in regions with limited internet or mobile service.
- Energy Efficiency: Consumes less power compared to traditional broadcast chains.
For IPTV operators, this model unlocks new territories — allowing providers to serve audiences beyond the limits of conventional broadband.
🌍 Real-World Applications
In 2026, several European and Asian broadcasters have already begun pilot projects combining Direct-to-Dish delivery with cloud-based content management. Users can now download on-demand shows, access interactive guides, and receive AI-curated recommendations — all via a single satellite connection.
This approach bridges the digital divide, providing high-quality entertainment to rural areas while reducing reliance on expensive infrastructure upgrades.
🟨 Reality Check
While Direct-to-Dish 2026 is revolutionary, its deployment requires new receiver standards and regulatory approvals for frequency sharing. Some markets also face challenges in balancing cost and accessibility — especially during the transition from legacy equipment to smart dishes.
However, as mass production scales and AI calibration becomes automatic, costs are expected to drop sharply by late 2027, making this technology mainstream for IPTV and satellite broadcasting alike.
🚀 The Future of Viewer Access
By 2028, experts predict a full merger between Direct-to-Dish and IPTV systems — creating a unified satellite-to-home ecosystem that delivers both live and on-demand content without any middle layers.
From personalized streaming to AI-driven advertising, D2D is paving the way for a world where every viewer is directly connected to space — not the grid.
🟥 Final Verdict
Direct-to-Dish 2026 is redefining how we connect to entertainment. By cutting out intermediaries and optimizing signal delivery through AI, it ensures seamless, high-quality access for everyone, everywhere.
In 2026, the dish is no longer just an antenna — it’s a gateway to the future of global broadcasting.